Growing garden crops in greenhouse conditions is widely popular not only among industrial suppliers of vegetables, but also among many summer residents and gardeners. After all, many are attracted by the idea of getting fresh tomatoes throughout the year, regardless of the season. However, despite the favorable conditions of greenhouses, the cultivation of tomatoes requires strict adherence to the basic rules of the process - from soil preparation to care procedures. Only in this case, the grower is waiting for a rich and high-quality harvest.
Optimal timing and time for transplanting seedlings
Choosing the best time for planting tomatoes, it should be borne in mind that during this period the seedlings must be at least 55-60 days old. It is better if the first flower brush is already formed on the seedlings, which gives a guarantee of an early and less painful engraftment.
It is better if the first flower brush is already formed on the seedlings, which gives a guarantee of an early and less painful engraftment.
The soil during planting should be warmed up to a temperature of +15 ... + 17 ° C. If the greenhouse is not heated, the soil is heated by covering the beds with a plastic film.
Did you know? Tomatoes can cheer up, because they contain a large amount of serotonin, which is also called the "hormone of happiness."
Despite the fact that in the conditions of a heated polycarbonate greenhouse, tomato cultivation can be practiced both in winter and in summer, nevertheless, the natural cycles of plant development should not be neglected, but so:
- seedlings in a heated room can be planted in the spring, at the end of April;
- if there is no heating in the greenhouse, but its coating consists of a double dense film, then seedlings are planted in the ground in early May;
- seedlings are planted in an ordinary film greenhouse in the second half of May.
Works in the greenhouse
Preparatory work is an extremely important stage in the cultivation of tomatoes, which will become the foundation for the quality of the future crop.
Greenhouse preparation
Today, polycarbonate greenhouses have almost completely replaced their film and glass predecessors. However, although the use of such structures has a lot of advantages, the farmer still needs to carefully familiarize himself with the specifics of the material and the technical features of such a greenhouse in order to be able to organize the most acceptable microclimate for growing tomatoes.
Important! It is necessary to constantly ensure that condensation does not form on the walls of the greenhouse, which can cause late blight. This is precisely the goal of systematic ventilation.
So, preparing the greenhouse for planting seedlings, the grower should consider:
- Ventilation - necessarily plentiful and regular. The best option would be a design that has not only side, but also upper vents (preferably in the amount of 3 pieces). Of course, it is also desirable to have an automatic device that independently opens the ventilation holes in case of exceeding the temperature regime inside the greenhouse.
- Preventative treatment - acts as a defense against the appearance and propagation of fungal infections, pest attacks and the prevention of putrefactive formations.
- Lighting - referring to photophilous crops, tomatoes react sharply even to small shading.
- Humidity level - 60–70% is considered the best indicator. You should know that excess moisture can provoke the formation of putrefactive diseases, and a decrease - the adhesion of pollen and the impossibility of rash from pollen bags.




Preparation of soil and beds
7–10 days before the proposed seedling planting, the preparation of beds is carried out - their width is 60–90 cm, and the height is within 25–30 cm. It is recommended to leave aisles between the beds (70 cm is considered the most comfortable distance). An important stage in the preparatory work is the process of independent formation of the soil mixture, which refers to the significant advantages of growing vegetables in greenhouse conditions. The best type of soil for tomatoes is considered to be sandy loam soil, but the structure of other soils can be significantly improved.
The best type of soil for tomatoes is considered to be sandy loam soil, but the structure of other soils can be significantly improved.
Depending on the type of main soil, you need to make:
- clay soil - 1 bucket of humus and 1 bucket of peat per 1 m²;
- peat soil - 1 bucket of shavings, humus, sod land, and 1/2 bucket of coarse sand per 1 m²;
- chernozem - 1 bucket of humus and 0.5 buckets of coarse sand per 1 m².
After the formation of the soil, fertilizers should be added to it, which will create an optimal nutrient medium for the growth and development of plants: 3 tsp are added to 1 m² of land. ammonium nitrate, 3 tbsp. superphosphates, as well as wood ash. Even before planting, the prepared soil should be decontaminated - for this, the soil is watered with a weak solution of potassium permanganate (1 g of potassium permanganate is dissolved in 10 l of water heated to + 60 ° C).
Even before planting, the prepared soil should be decontaminated - for this, the soil is watered with a weak solution of potassium permanganate (1 g of potassium permanganate is dissolved in 10 l of water heated to + 60 ° C).
Preparing seedlings for planting
Before planting seedlings for a permanent place in the greenhouse, it will require some preparation, which consists of several basic procedures:
- Pick - carried out immediately before planting and significantly accelerates the growth and development of the plant. To do this, carefully seedl out the seedlings from a container with a lump of earth on the rhizome (it is best to use wooden sticks or a teaspoon for this purpose). Next, the plants are separated and planted in a new place.
- Hardening - It enables plants to develop correctly, even in unsuitable conditions, and also activates immunity to various diseases. Such preparation must begin to be carried out 2–2.5 weeks before the expected date of transplanting seedlings to a permanent place.
 To do this, in the daytime and at night, the window leaves are left open in the greenhouse, and if the air warms up to + 12 ° C, the seedlings are taken out into the open air.
To do this, in the daytime and at night, the window leaves are left open in the greenhouse, and if the air warms up to + 12 ° C, the seedlings are taken out into the open air.

Approximately 5-7 days before planting seedlings, all bushes are sprayed with a solution of boric acid, at the rate of 1 g of the drug per 1 liter of water. This procedure allows you to save the buds on the first flower brush, which means it guarantees a rich harvest. The optimal time is considered to be an early morning or a cloudy day. 3 days before planting on each bush, seedlings cut 3 lower leaves, which reduces the likelihood of developing fungal diseases and contributes to the active development of the first flower brush.
3 days before planting on each bush, seedlings cut 3 lower leaves, which reduces the likelihood of developing fungal diseases and contributes to the active development of the first flower brush.
Landing pattern
Landing is recommended in the morning or evening hours or on a cloudy day. You should know that the soil on the beds should be well moistened, and the seedlings themselves should not be too deep when planting. Pre-prepare holes up to 12 cm deep, and the plants themselves are carefully examined before planting, eliminating the possibility of damage.
Planting density directly depends on the selected tomato variety:
- low-growing varieties (formed in 2 or more stems) are planted using a checkerboard pattern - the row spacing is about 55 cm, and the distance between the bushes does not exceed 40 cm;
- cultivation of stamped and determinant varieties (with one main stem) allows planting to be somewhat denser - the distance between rows does not exceed 50 cm, and between bushes is 35 cm;
- indeterminate varieties suggest planting according to the pattern: row spacing - 40 cm, distance between plants - about 70 cm.
Important! If it is planned to plant different vegetables in one greenhouse that require different conditions of detention, the whole area should be divided into parts using a film and each should maintain its own microclimate.
What to do if seedlings outgrew
First of all, noticing the extension of seedlings, it should be correctly dived - cut off the upper part of the sprout 20 cm long, which is then again planted in a prepared container for rooting. To accelerate the formation of rhizomes, the trimmed fragment of the bush before planting is placed in the Kornevin solution (prepared according to the instructions). However, even overgrown seedlings can be planted in the ground. There are several main ways for this:
- Inclined - is one of the easiest ways that has proven itself when planting. According to this method, shallow holes are dug (not more than 10 cm), in which humus is placed and water is poured. After complete absorption of moisture, the overgrown bush of seedlings with the previously removed lower foliage is laid in a hole at an angle (the length of the upper part does not exceed 30 cm). The plant is again watered and mulched. This method of planting involves extremely careful loosening later, since the root system of tomatoes is very close to the surface of the earth.
- Dry way Kazarin - using this method, furrows with a depth of 10-15 cm are preliminarily prepared in the beds, to which humus and a potassium permanganate solution are added. The soil is well watered, and in the prepared bushes, seedlings remove the lower leaves. Plants in trenches are laid almost horizontally, sprinkled with earth and watered again. The essence of the method is the complete absence of further watering throughout the season. This method will stimulate seedlings to actively develop the root system in an attempt to get to moisture. At first, the plant will continue to grow horizontally, but over time, the crown will take a vertical position.
- Maslov Method - relies on the possibility of tomato bushes to take new roots along the stem, which is in the ground. In prepared furrows 12 cm deep, seedlings are placed in such a way that not only the root, but also part of the stem is in the soil mixture. Planting occurs strictly from south to north, and already in the process of growing the tops of the bushes will involuntarily stretch to the south, acquiring a vertical position.


Subsequent care of tomatoes after planting
It is believed that tomatoes are unpretentious crops, and therefore do not require special care. However, even minimal care for these plants will bring its results in the form of a rich and high-quality crop.
Watering
The first time watering is carried out immediately after planting tomato seedlings in a permanent place, the soil should be moistened to a depth of about 20 cm. This will provide better interaction of the root system with the soil, while reducing the survival time. The second time the tomatoes are watered after 7–10 days and subsequently as the top layer of the earth dries.
During budding and flowering, the irrigation volume is reduced to 1.5 liters per plant, and the interval increases to 5–7 days. Such a strategy helps to restrain the growth of green mass, thereby stimulating the formation of new ovaries.
During the fruiting period, watering of tomatoes increases to 1 time in 2-3 days, and in conditions of intense heat - even to daily. In this case, soil moisture should reach 25-30 cm in depth. Drying of the soil during this period can be the main cause of cracking of the fruit. The most preferred method of watering tomatoes in polycarbonate greenhouses is drip irrigation.
The most preferred method of watering tomatoes in polycarbonate greenhouses is drip irrigation.
Loosening
Since the soil is the main source of nutrition for the root system, the soil on the beds needs constant care. One of the main stages is loosening - a procedure that allows you to enrich the soil with oxygen and maintain its moisture for a longer period. It is for this reason that it is recommended not to allow the formation of a crust on the soil after watering, but to immediately loosen it.
It is for this reason that it is recommended not to allow the formation of a crust on the soil after watering, but to immediately loosen it.
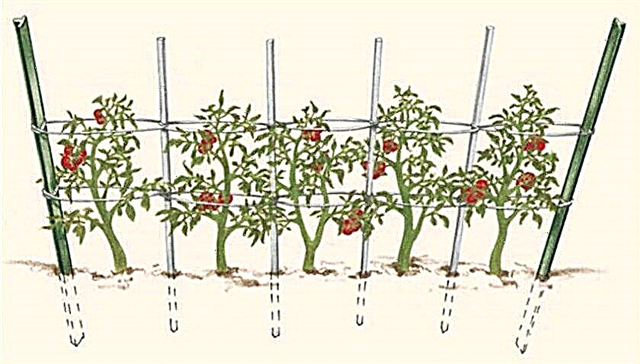
Tying
Due to the fact that the tomatoes tied to the support receive more uniform illumination and are also better ventilated, which minimizes the appearance and spread of fungal diseases, among the main stages of tomato care is the garter of the bushes. The procedure is carried out approximately 7-10 days after transplanting the seedlings to a permanent place, when it is fully acclimatized. There are 2 main ways to garter:
- Individual - each plant is tied to a separate support, which can be used wooden sticks, honed on one side, or pins made of metal or plastic (they are driven into the ground at a distance of 10 cm from the bush to a depth of about 40 cm). The bushes are attached to the supports using a rope or wire or plastic hooks, which can be purchased in specialized stores.
- Tapestry - stakes are installed throughout the entire bed, the distance between which is about 2 m. Between them stretch a wire or twine in several rows (the distance between the rows is 20-30 cm). It is to them that the bushes are tied. This method is considered more acceptable for tall varieties of tomatoes.

Stepson
During the growth and development of tomato bushes, the plant spends significant forces on providing nutrients to numerous lateral shoots on the bush. That is why, growing tomatoes, it is impossible to achieve great results in the crop, ignoring the pinching. It should be borne in mind:
- bushes of tall varieties are formed into one stem, and the side shoots are completely removed, the stem itself is pinched at the level of the seventh fruit brush;
- medium and undersized varieties usually form in 2-3 stems - there remains one additional shoot located above the first flower brush, and all other shoots located above the second brush are deleted.

Did you know? Despite the large amount of vitamins and nutrients, a tomato is 95% water.
Top dressing
Adhering to the basic rules of agricultural technology for growing tomatoes, this crop will not need special care. However, top dressing is the main factor affecting the growth and development of plants. Often, tomatoes are fertilized with the following nutrient solutions:
- mullein - the manure is poured with water and insisted for 5-7 days, after which it is diluted with a bucket of water (top dressing is carried out at the rate of 1 liter for each bush);
- chicken droppings - cooking technology is identical with mullein;
- green infusion - 1 bucket of manure, 5 kg of weed grass and 1 glass of ash are poured into 50 liters of water and insisted in the sun for a week, after which they are filtered and diluted with 100 liters of water (1 liter of infusion is applied under 1 plant);
- combined - prepared with 1 liter of mullein, superphosphate (1 box of matches) and 1/2 cup of ash diluted in 10 liters of water (0.5 liter of solution is poured under each bush);
- chemical - used as the first top dressing, consists of ammonium nitrate and urea.
Video: feeding tomatoes
If during growth tomatoes require nitrogen fertilizers, which are necessary for gaining green mass, then during flowering fertilizers consist mainly of potassium and phosphorus. At the same time, foliar top dressing, which is carried out every 7–9 days, is considered the most effective. During this period, superphosphates (based on 2 tablespoons per 10 liters of water) and potassium monophosphate (2 tablespoons are diluted in 10 liters of water) are used for tomatoes. Complex fertilizers and treatment of plants with a solution of boric acid (5 g or 1 hour are dissolved in 10 l of water) are also used as top dressing, which stimulates the formation of ovaries.
In addition, experienced farmers often use top dressings prepared according to folk recipes:
- solution with milk and iodine - 1 liter of milk and 15 drops of iodine are dissolved in 10 liters of water;
- yeast fertilizer - in 1 bucket of water add 10 g of yeast and 2 tablespoons of sugar (fertilizing is applied to the soil);
- mortar with wood ash - 1 liter of ash is poured into 1 liter of boiling water and cooled, after which it is diluted with water to a volume of 10 liters;
- nettle infusion - nettle boil for 10 minutes and then insist for 10 hours.
 An important feature of proper top dressing is its introduction only after watering the tomatoes.
An important feature of proper top dressing is its introduction only after watering the tomatoes.Tips from experienced gardeners
Having familiarized with the basic information on planting and further growing tomato seedlings, It will be useful to heed the advice of experienced gardeners, since their knowledge is primarily based on extensive experience:
- Starting in the spring of preparatory work, it is recommended to put last year’s not rotted compost under the lower soil layer - in this case, it will play the role of additional heating for seedlings, and in the future will serve as top dressing.
- In the process of planting seedlings, all leaves that are at ground level, as well as yellowed and having signs of illness, must be removed. It is better to carry out such a procedure in the morning.
- Lack of nutrients can be determined by foliage. When folding the leaves and the appearance of the border, it is necessary to add potassium to the soil. Raising the leaves and acquiring them with the back of a purple hue signals a lack of phosphorus. With a lack of magnesium, the leaves become marbled.


Summing up, it is worth noting that the process of growing tomatoes in polycarbonate greenhouses is a rather time-consuming and troublesome matter, because it requires not only the basic rules for caring for tomatoes to be followed, but also the necessary conditions in the greenhouse itself. However, having spent time and effort, each gardener will be able to get a rich and high-quality crop, regardless of the time of year.


 To do this, in the daytime and at night, the window leaves are left open in the greenhouse, and if the air warms up to + 12 ° C, the seedlings are taken out into the open air.
To do this, in the daytime and at night, the window leaves are left open in the greenhouse, and if the air warms up to + 12 ° C, the seedlings are taken out into the open air.